Scabies is a highly contagious skin infection that affects the human body with traces of rashes after being infected.
It is categorized as a skin condition caused by Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis, birthing discomfort, which leads to intense itching.
When this skin condition is left untreated, scabies can spread rapidly among individuals in close contact, making it crucial to understand its symptoms, transmission, treatment, and prevention.
In 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced that at least 200 million people suffer from scabies worldwide at any one time and 400 million people per year, leaving children the most vulnerable victims of scabies.
WHO estimated that 5 to –50% of children in underdeveloped areas are affected by scabies and can be transmitted in hot, tropical countries and in areas of high population density.
Scabies in 2017 was added to Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) by the WHO.
Causes of scabies
Scabies occurs when the female mite burrows into the skin to lay eggs. This triggers an allergic reaction that causes the hallmark itching and inflammation. The mites are so small that they are nearly impossible to see with the naked eye, but their presence is enough to wreak havoc on the skin.
How Do Scabies Spread?
Scabies is primarily spread through prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. This makes it particularly common in crowded living conditions, such as families or households, schools and daycare centres, nursing homes, and prisons.
Symptoms of Scabies
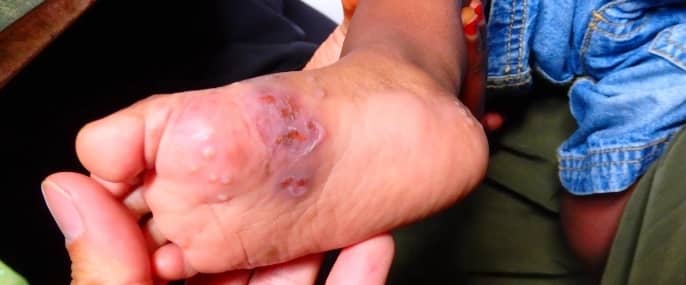
The signs of scabies usually appear within three to six weeks after initial exposure. Key symptoms include: intense itching, especially at night. Rashes are usually small, red bumps or blisters that often form in a line or track, and burrow marks.
Commonly affected areas include: between the fingers, wrists, and elbows, armpits, around the waist and groin, and on the buttocks and thighs.
For infants and young children, scabies may also appear on the scalp, face, neck, palms, and soles.
Home Care and Management
In addition to medical treatment, proper hygiene and cleaning are essential to eliminate mites.
Prevention Tips
To prevent scabies, one needs to follow these steps critically:
- Avoid prolonged physical contact with infected individuals.
- Do not share personal items like towels, bedding, or clothes.
- Practice good hygiene and maintain a clean environment.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is advisable to seek medical assistance immediately whenever you or a family member experiences persistent itching or rash.
Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent complications such as bacterial skin infections caused by excessive scratching.
However, scabies is a treatable condition, but its highly contagious nature makes awareness and prompt action vital. With proper medical care, hygiene practices, and preventive measures, you can effectively manage and stop the spread of this skin infection.